Background
The Clinic’s Doctor found his nurse, Ms Cheung, kept calling in sick lately, so he wanted to check her medical record held at public hospital via eHealth.

Dr Kam, have you seen Ms Cheung? I got something to tell her.
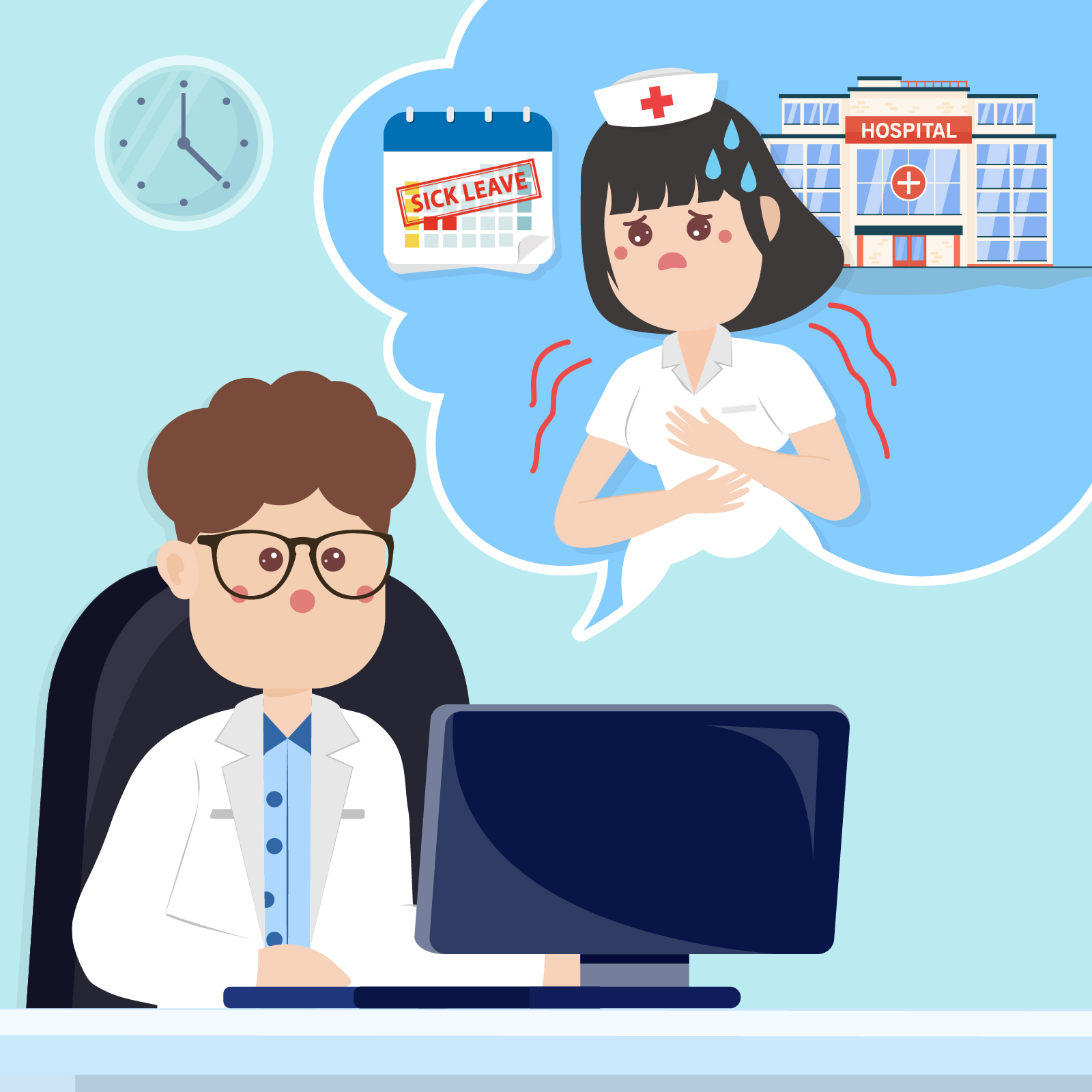

Ms Cheung is on sick leave today.
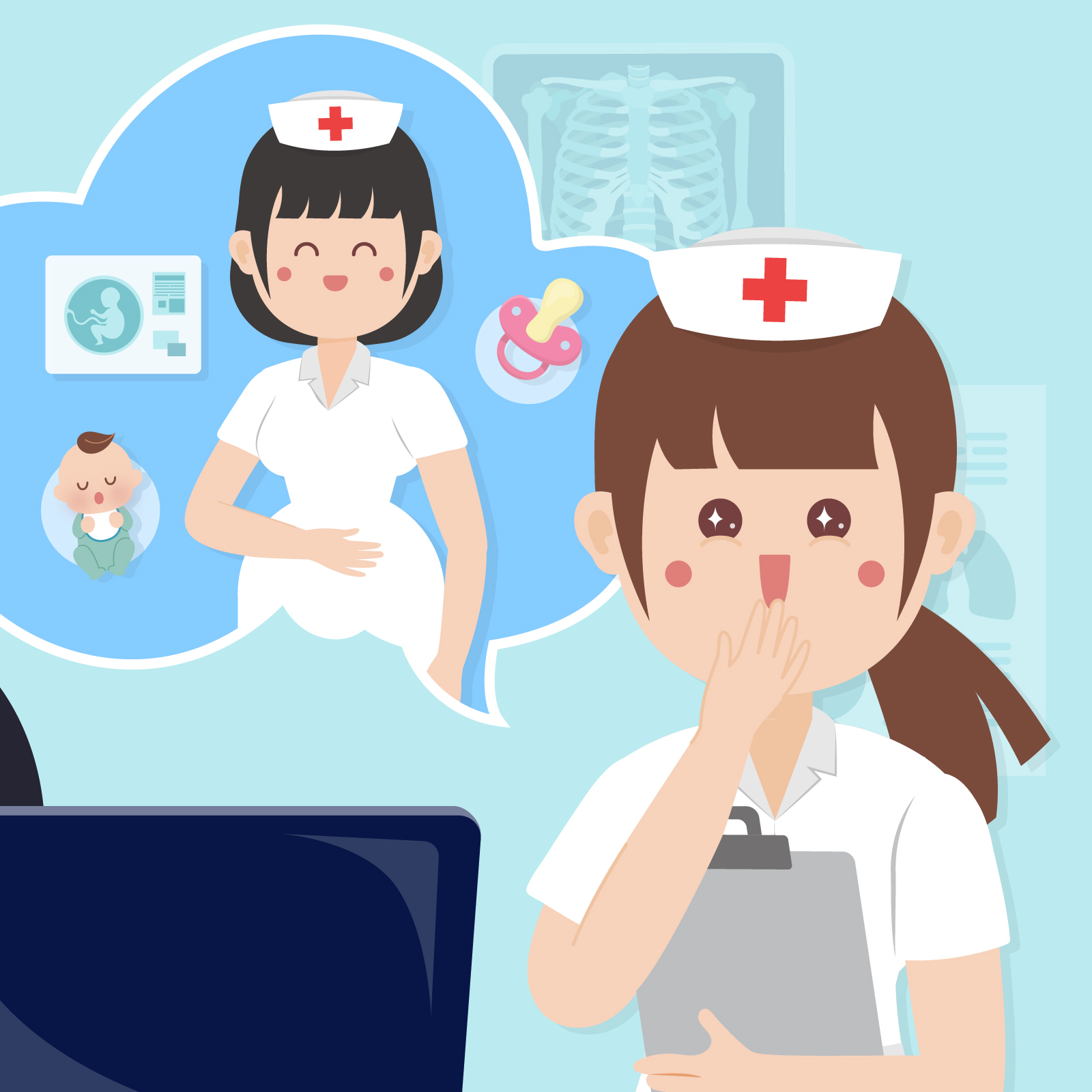

She has been throwing up and calling in sick these days. Oops…… very likely that she’s pregnant!
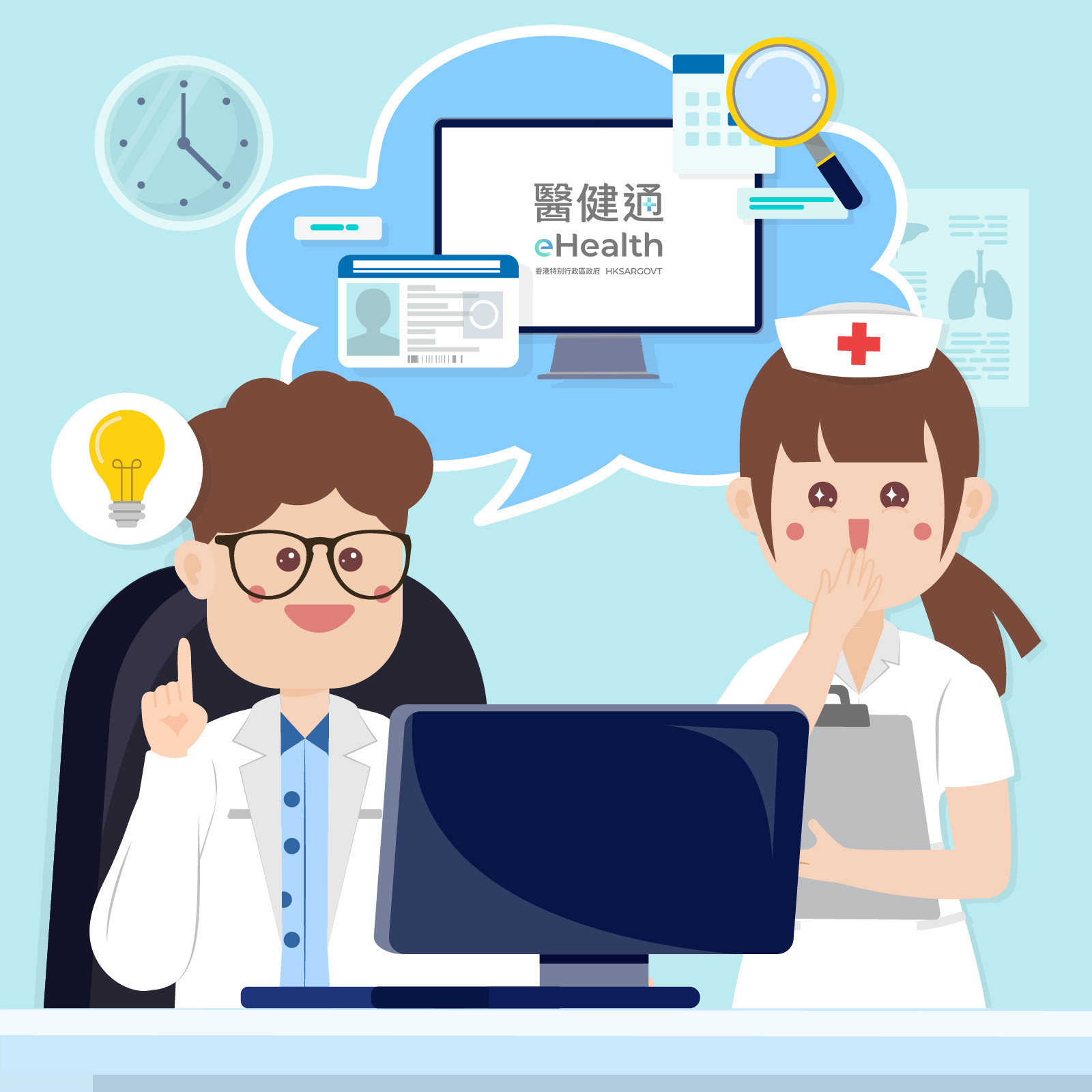

Easy peasy. She had already joined eHealth and given sharing consent to our clinic. Let me check her record.
Answer: C
According to section 2.4.5 of the “Code of Practice for Using Electronic Health Record for Healthcare”, healthcare providers should ensure that only authorised healthcare professionals with the “need-to-know” can access the eHRs of healthcare recipients under their care in accordance with their pre-defined professional roles and access rights.
Background
Recently, the clinic has been recruiting a full-time patient assistant. The doctor viewed the applicant Ms Wong’s eHR while she was attending the interview.
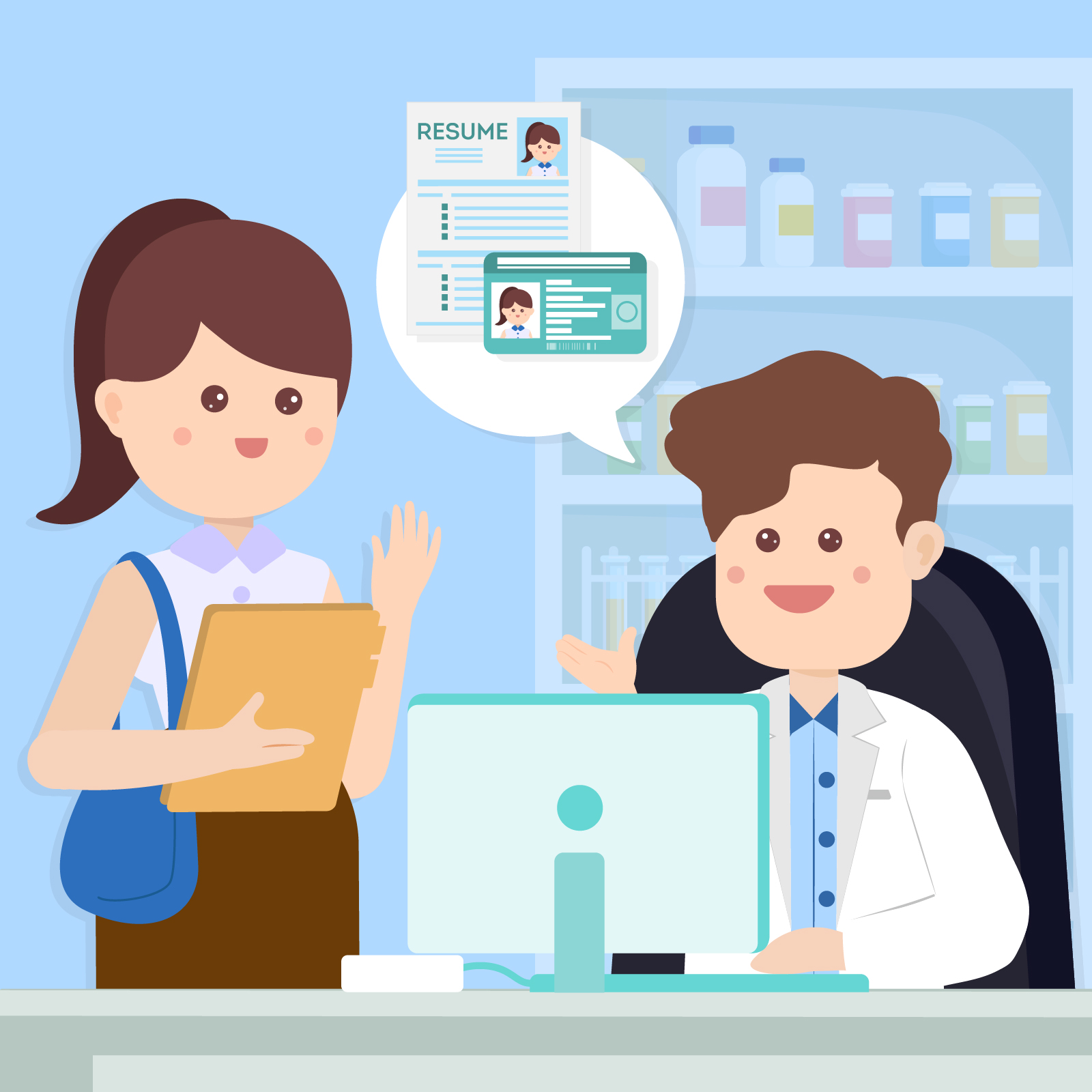

Hello, I’m here to apply for the post of patient assistant.
Ms Wong, would you please provide us your HKID card and resume?

Ms Wong passed the HKID card and resume to Dr Lau.
Thanks. Please introduce yourself and your past working experiences.

Uh~Ah~I……

Dr Lau thought that Ms Wong was quite mentally unstable during the interview. He wanted to access her eHR to learn about her physical and mental health status, so as to consider whether to hire her.
Answer: C
According to the section 3.3.4 of the “Code of Practice for Using Electronic Health Record for Healthcare”, healthcare professionals should only access eHRs of healthcare recipients with their expressed and informed sharing consent and there is a need-to-know about the healthcare recipients’ health conditions according to their roles of providing healthcare to the healthcare recipients.
Background
Since there are many nurses and clerical staff in a hospital, the Manager, Mr Chan, shared his eHealth user account information with his colleagues at the registration counter for carrying out administrative works.


Mr Chan, it’s my first day of work here and I don’t have an eHealth user account. How can I assist the doctors in handling the patients’ sharing consents, so as to facilitate them in accessing the patients’ electronic health records (eHRs)?
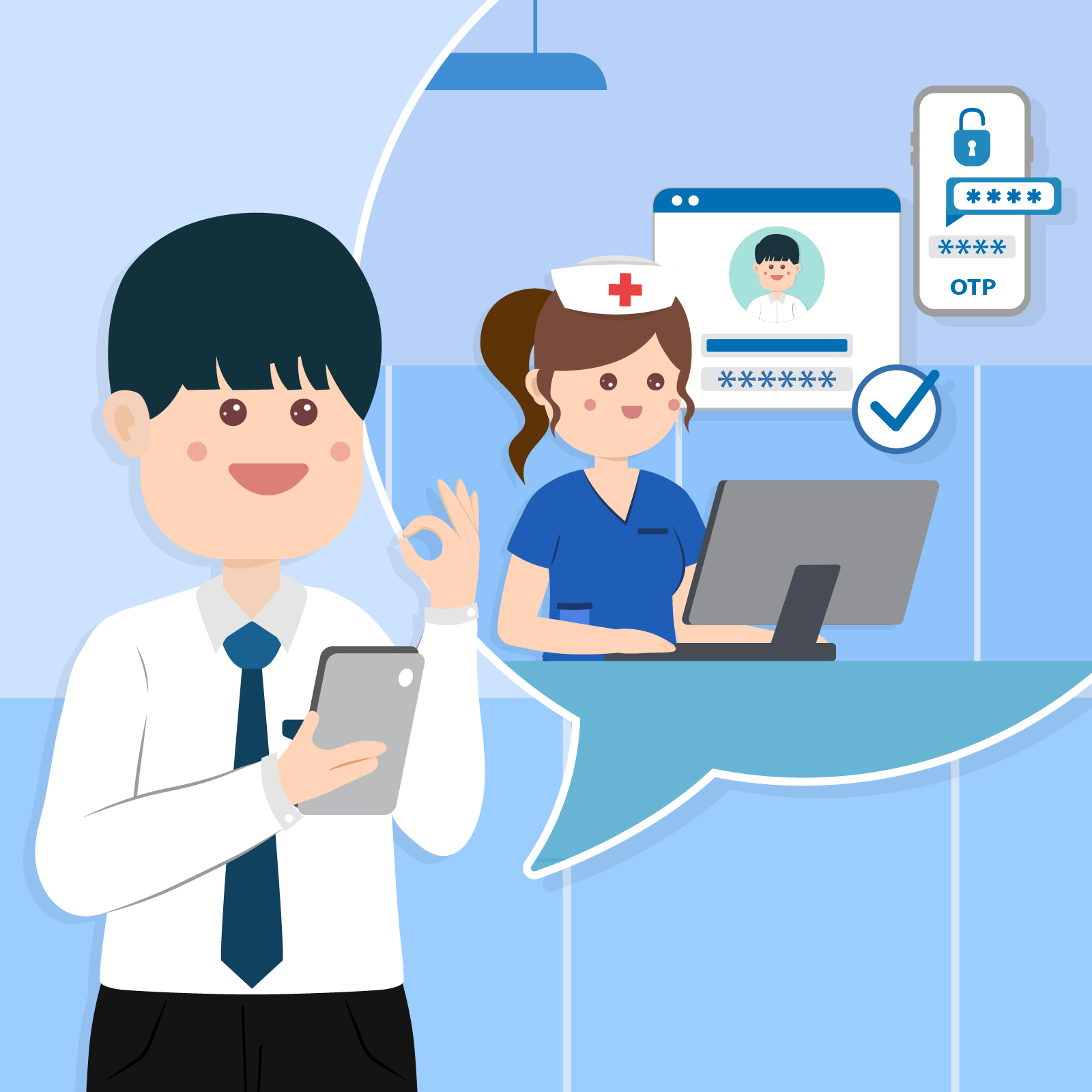

No worries! Just like you, the other colleagues working at the registration counter do not have individual eHealth user account. They used to log in eHealth with my account. You can ask them for my login credentials. I have also put the mobile phone at the counter for colleagues to receive the one-time-password for logging in the system easily.
Answer: C
The user account of eHealth is on an individual basis. For system security and privacy reasons, sharing of user account is prohibited. Users should access eHealth only with their own accounts and should not disclose or share usernames and passwords with other users. Each access to the eHRs of healthcare recipients will be logged, monitored and audited. Healthcare recipients will receive a notification for any access to their record.
Protection of data privacy and system security
Given the sensitive nature of health data, we attach paramount importance to data privacy and system security of the Electronic Health Record Sharing System (eHealth), and have put great effort to safeguard them. In addition to the establishment of an eHealth-specific legislation, security measures are implemented in technical and operational aspects.
-
Role-based access control
Expand
It is a built-in differentiated access control to regulate the access of authorised healthcare professionals, with features as follows:
- Different authorised healthcare providers have different levels of access to data and functions.
- Pre-defined differentiated access rights set in accordance with the clinical need or function of different healthcare professionals.
- Access to parts of electronic health record (eHR) only relevant to their professional service under the "need-to-know" principle.
- All access will be logged properly and subject to audit and inspection.
-
Data validation and encryption
Expand
- Imported eHR data will be validated to avoid inputting errors.
- Important patient demographic data such as HK identity card number, date of birth and sex, and other significant data like drug code will all be validated.
- All eHR data in the databases, files, archives and during transmission is encrypted.
- High-security encryption will be applied to guard against unauthorised access.
-
Authentication of patients and healthcare providers
Expand
Patients
- Identified by a centralised Person Master Index to ensure health data are correctly associated with individual concerned.
- Authenticated patients properly for giving consent and authorisation.
Healthcare providers
- Identified and authenticated through a centralised database to ensure eHR data uploaded are attributed correctly.
- All activities through the eHealth, including access and changes to data, are logged properly.
- Verify the professional status of all healthcare professionals participating in eHR sharing.
-
Security monitoring and audit
Expand
Healthcare providers
- Perform regular audits on their own electronic medical record / electronic patient record (eMR / ePR) systems.
- Mitigate any security breaches or loopholes and report to eHR Commissioner promptly.
- Log all access to the eHealth to facilitate regular or random audits.
eHR Commissioner
- Perform security audits on the eMR / ePR systems and the internal access control of healthcare providers.
- Suggest mitigating measures for healthcare providers.
-
Access notification to patients
Expand
Patients will receive notification via short message service (SMS) or other means under the following scenarios -
- Access to patient's eHR with consent.
- Access to patient's eHR which is under restricted control with additional consent*.
- Attempt to access patient's eHR after expiry of patient's consent to healthcare providers.
- Access to patient's eHR without consent under exceptional circumstances (e.g. emergency situations).
- Security concern that may affect patient's eHR.
-
Restricted downloading of electronic health record (eHR) data
Expand
- To minimise the risk of data leakage, downloading of eHR data is restricted.
- Only Person Master Index data and allergy / adverse reaction information can be downloaded as they are essential to seamless authentication of patients and vital clinical decision support.
- Other eHR data, such as diagnosis and episode summary, can only be viewed from the eHealth, but not downloaded.
-
Safeguard the patient rights
Expand
- Patient Information Notice will be provided to patient.
- Healthcare providers can only share patients' eHR data with their express and informed consent.
- Patients or their substitute decision makers may request for data access and correction.
eHealth Quiz Challenge
Frequently asked questions
-
What is "patient-under-care"?Expand
- Any authorised user of eHealth shall only access information of any patient for providing healthcare.
- Healthcare may include activities performed by a healthcare professional for assessing, recording, maintaining or improving the health, diagnosing and treating an individual.
-
What is "need-to-know"?Expand
- Any authorised user of eHealth shall only access information of any patient he / she needs to know in the course of providing healthcare to the patient.
- Need-to-know for different users shall be justified according to their roles in providing care to the patient.
-
Who can access my eHR and what kind of information can be accessed?Expand
- Only staff who works under healthcare providers with your sharing consent, providing you healthcare and with the need-to-know will be allowed to access your health information. All access will be logged and you will receive notification through the communication means you chose whenever your eHR is accessed.
- Only the healthcare professional staff taking care of you is allowed to access your health record and on a need-to-know basis.
- Administrative staff is not allowed to view health records of patients and can only have limited access rights to personal particulars used for patient registration.
-
What measures are in place to ensure security of eHealth?Expand
- Technical facilities (e.g. anti-virus, intrusion detection / prevention, firewall, data encryption, user authentication, digital certificates etc.) provide necessary protection to eHealth.
- All access activities will be logged in eHealth to allow detection and tracking of improper data access.
- Security policies and control procedures are established and appropriate technologies are also employed to safeguard data security and minimise the risk of leakage of personal health data.
- Security risk assessment and audit on eHealth are arranged to ensure that eHealth are properly protected against prevailing security threats.
- eMR systems of healthcare providers are registered and security compliance is required for their connection to eHealth.
- Code of Practice, procedures, guidelines and briefings are provided to healthcare providers and their staff for security awareness, and assist them in properly accessing to and using patient's information.


